Living Well with Diabetes: Self-care and Support
Managing diabetes is a lifelong journey that requires consistent self-care and support. By adopting self-care practices and seeking appropriate assistance, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their condition and live a fulfilling life. Here, we explore key strategies for living well with diabetes. Living well with diabetes requires a holistic approach that encompasses self-care, support, and ongoing education. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, adhering to treatment plans, seeking emotional support, and staying informed, individuals can effectively manage their condition and lead a fulfilling life. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals and engage in self-care practices that support both physical and emotional well-being.
Diabetes and Mental Health: Nurturing Emotional Well-being
Living with diabetes can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health and emotional well-being. The daily management tasks, the need for strict self-care routines, and the constant vigilance over blood sugar levels can lead to feelings of stress, anxiety, and even depression. Understanding the connection between diabetes and mental health is crucial for individuals to take proactive steps in nurturing their emotional well-being. Here, we explore strategies to promote mental health while managing diabetes. By prioritizing mental health and nurturing emotional well-being, individuals with diabetes can enhance their overall quality of life. Recognizing the impact of diabetes on mental health and adopting strategies to manage stress and emotions are crucial steps toward a balanced and fulfilling life with diabetes. With the right support and self-care practices, individuals can effectively manage both their physical and emotional well-being.
Complications of Diabetes: Understanding the Risks
Diabetes is a chronic condition that, when not effectively managed, can lead to various complications. High blood sugar levels over time can damage blood vessels and organs, increasing the risk of long-term health issues. Understanding the potential complications associated with diabetes is crucial for individuals to take proactive steps in their management and seek appropriate medical care. Here, we explore some common complications of diabetes. It is important to note that with proper management, the risk of complications can be minimized. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, adhering to medication and treatment plans, adopting a healthy lifestyle (including a balanced diet and regular exercise), and seeking regular medical care are key in preventing and managing diabetes complications. Individuals with diabetes should work closely with their healthcare team to develop an individualized plan to address their specific needs and reduce the risk of complications. By managing blood sugar levels effectively and…
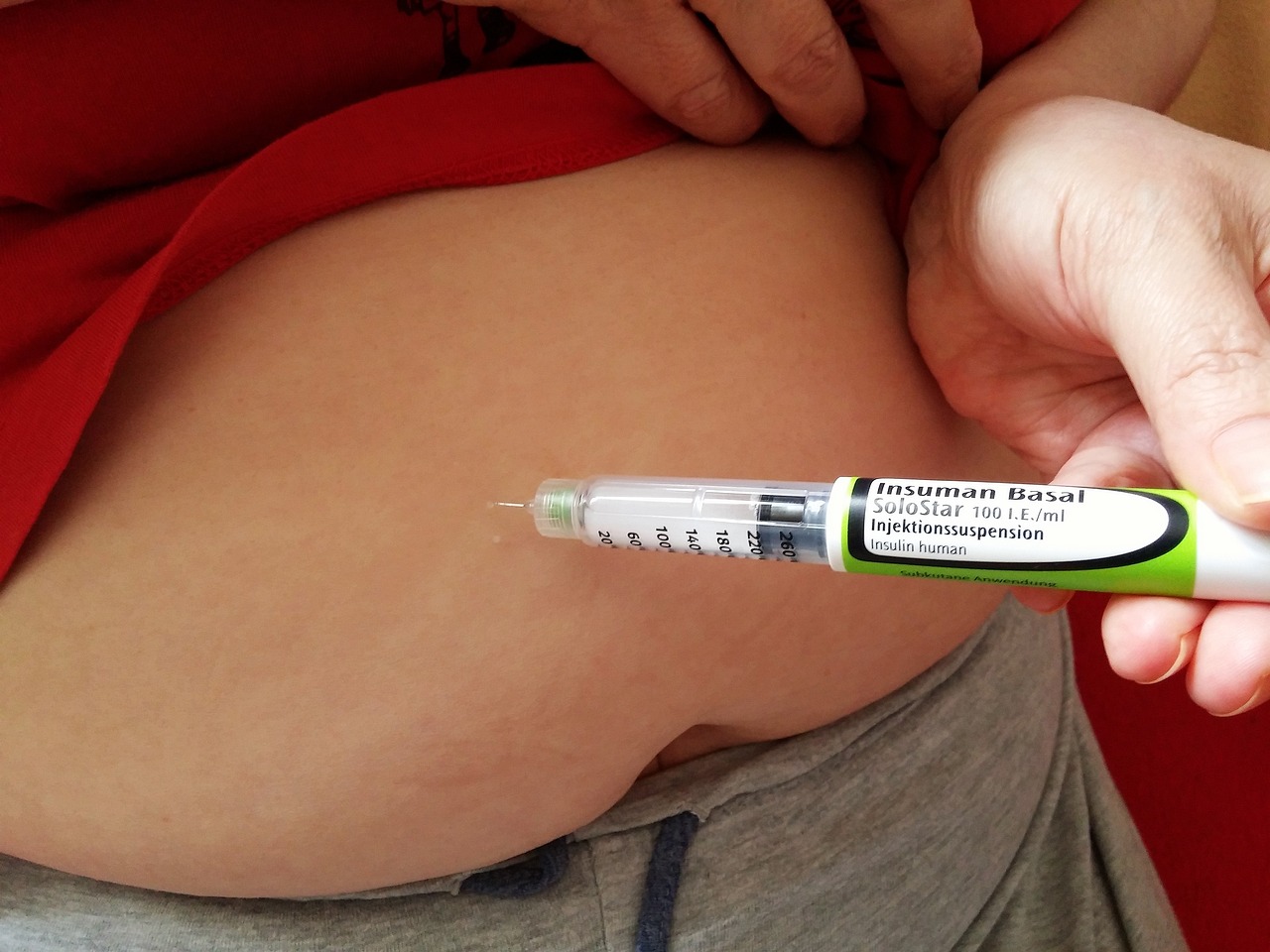
Medications for Diabetes: Types and Usage
Diabetes is a chronic condition that often requires medication to help manage blood sugar levels effectively. There are various types of medications available, each with its mechanism of action and specific usage. Understanding the different types and their purposes can help individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about their treatment plans. Here, we explore some common medications used in diabetes management. It’s important to note that medication choices and usage vary depending on an individual’s specific needs, diabetes type, medical history, and other factors. Treatment plans are typically determined by healthcare professionals, including doctors and diabetes educators, who can assess an individual’s condition and prescribe appropriate medications. Adherence to medication schedules, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, and open communication with healthcare providers are essential for optimal diabetes management. By working closely with their healthcare team, individuals with diabetes can find the medication regimen that best suits their needs and…
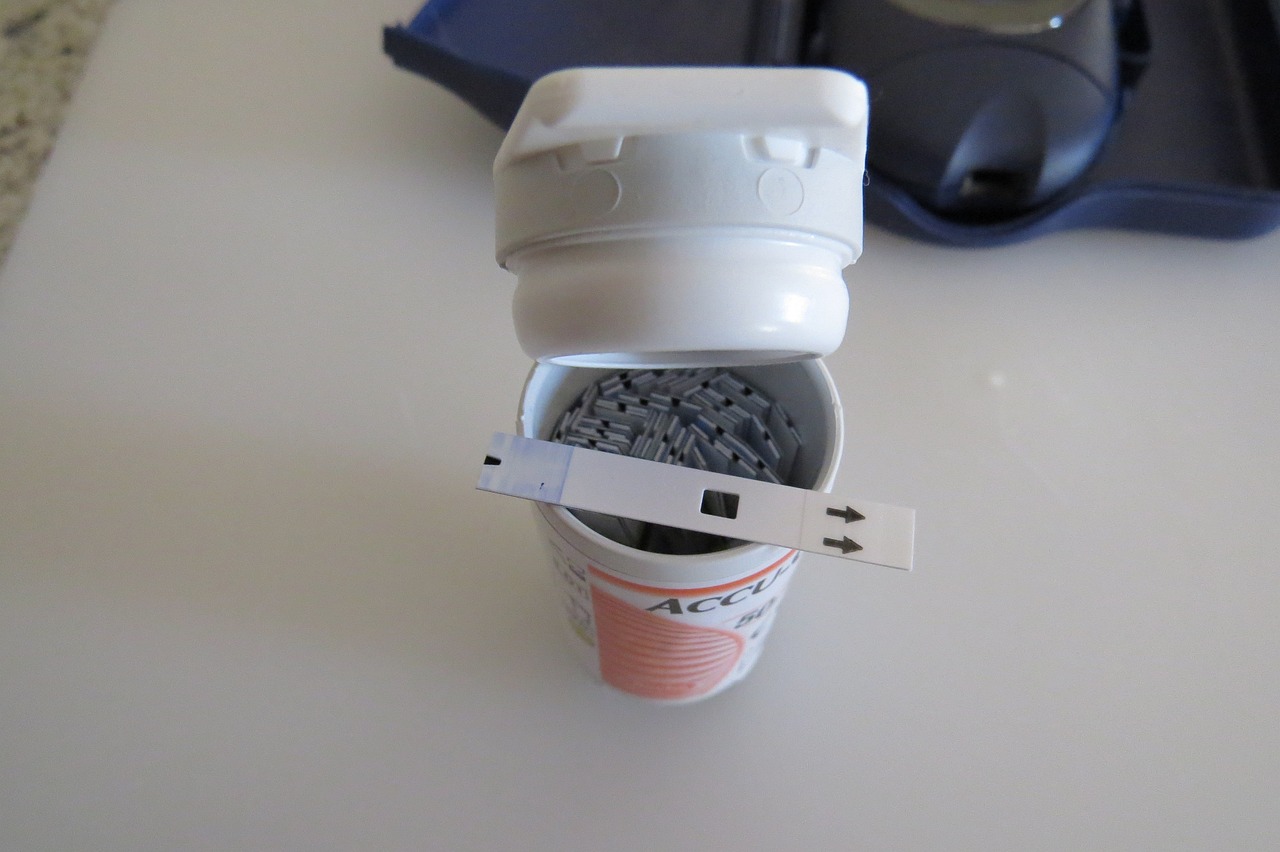
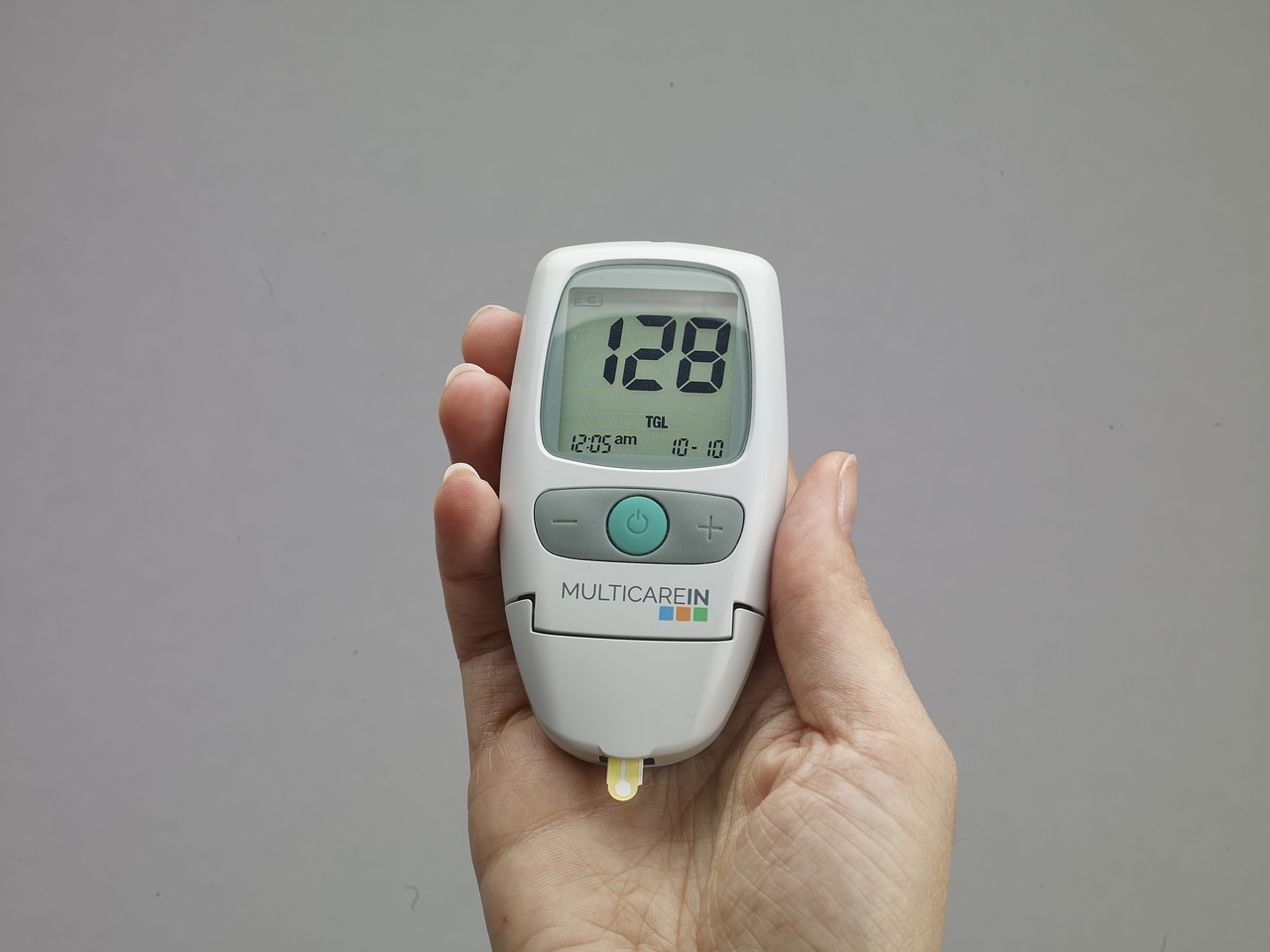
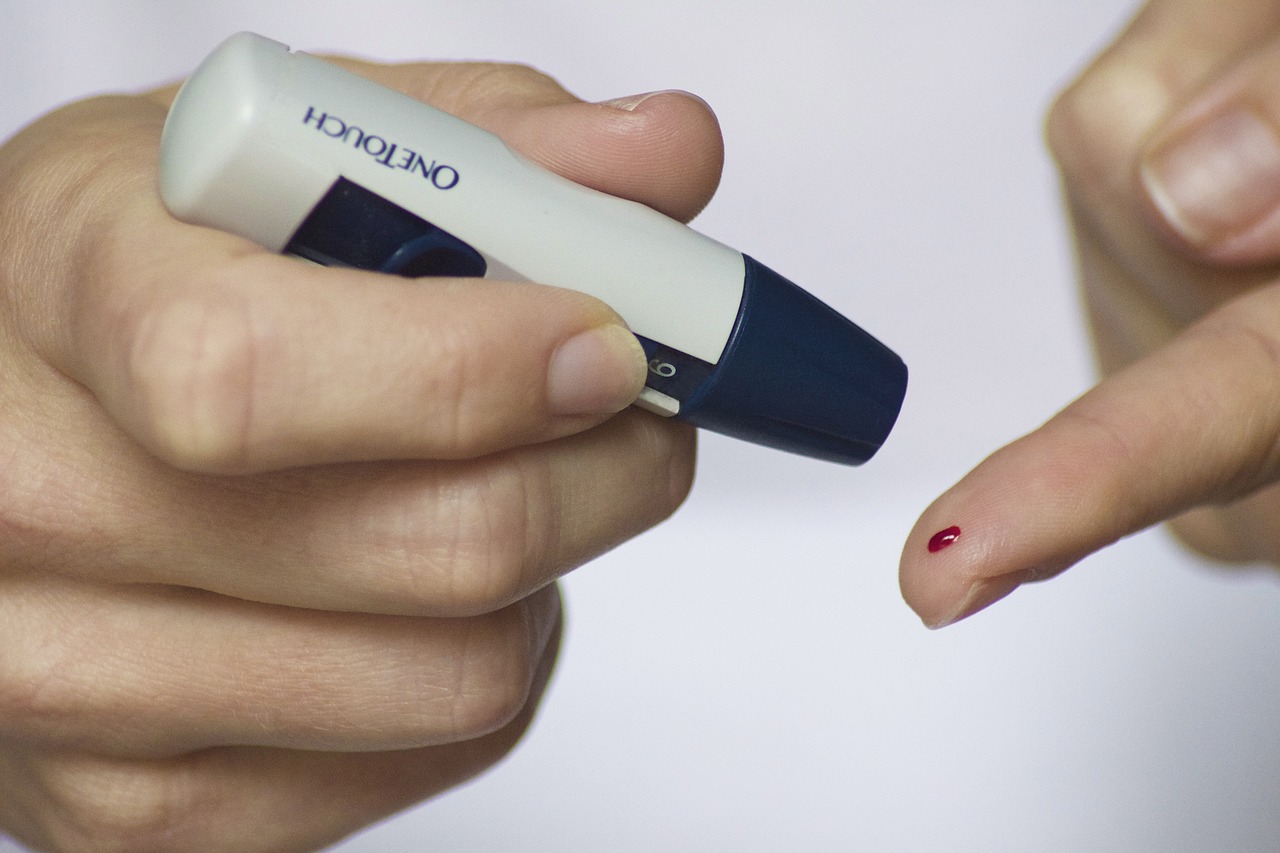
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Tools and Techniques
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of diabetes management. Regular monitoring allows individuals to track their glucose levels, make informed decisions about medication dosages, and adjust their lifestyle choices accordingly. Here, we will explore various tools and techniques available for monitoring blood sugar levels accurately. In addition to the tools mentioned above, individuals can adopt various techniques to optimize blood sugar monitoring: By utilizing appropriate monitoring tools and techniques, individuals with diabetes can stay informed about their blood sugar levels, make informed decisions about their diabetes management, and achieve better control over their condition. Regular monitoring empowers individuals to take charge of their health and make proactive choices to maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
Exercise and Diabetes: The Power of Physical Activity
Regular exercise is a powerful tool in the management and prevention of diabetes. Physical activity not only helps control blood sugar levels but also improves insulin sensitivity, aids in weight management, reduces the risk of cardiovascular complications, and enhances overall well-being. Here’s a closer look at the benefits of exercise for individuals with diabetes. One of the primary benefits of exercise is its impact on blood sugar regulation. When muscles are active during exercise, they take up glucose from the bloodstream to use as fuel, which helps lower blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, making the body’s cells more responsive to the insulin produced by the pancreas. This can lead to better glycemic control and reduced reliance on diabetes medications. Exercise also plays a vital role in weight management. Obesity is a significant risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes and can make blood sugar control…
Diabetes and Diet: Making Healthy Food Choices
Diet plays a fundamental role in managing diabetes effectively. Making healthy food choices can help individuals regulate their blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Here are some key principles to consider when it comes to diabetes and diet. Carbohydrate counting is an essential component of diabetes meal planning. Carbohydrates directly impact blood sugar levels, so it’s crucial to monitor and control carbohydrate intake. Choosing complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, over simple carbohydrates like sugary snacks and refined grains, can help stabilize blood sugar levels. It’s also important to pay attention to portion sizes to avoid consuming excessive carbohydrates in one sitting. The glycemic index (GI) is another tool that can assist individuals in managing their diet. The GI measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI, such as white…
Understanding Diabetes: Types, Symptoms, and Risk Factors
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. It occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or doesn’t effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels. There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that usually develops in childhood or adolescence. In this condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes require daily insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump to survive. Common symptoms of type 1 diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, extreme fatigue, and blurred vision. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for around 90% of cases. It usually develops in adulthood, although…