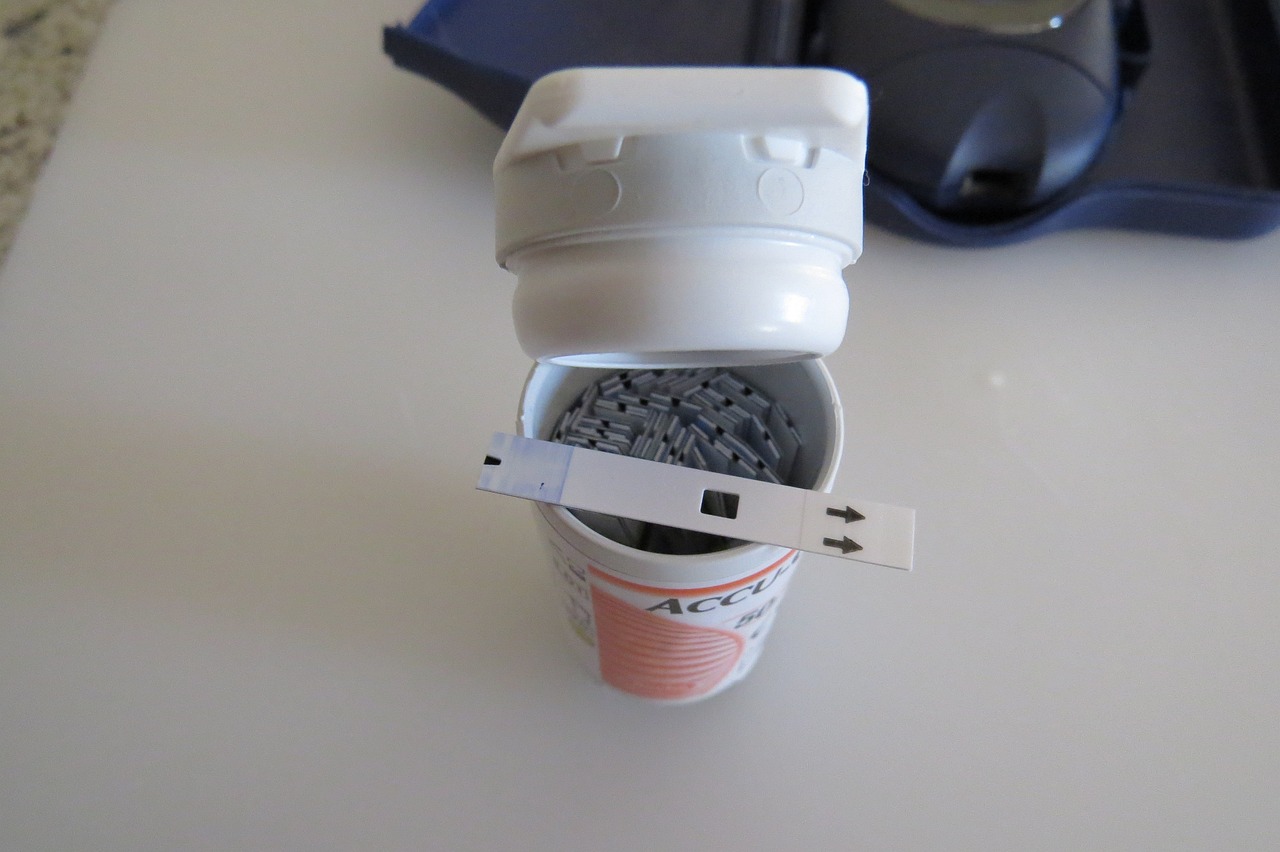
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of diabetes management. Regular monitoring allows individuals to track their glucose levels, make informed decisions about medication dosages, and adjust their lifestyle choices accordingly. Here, we will explore various tools and techniques available for monitoring blood sugar levels accurately.
- Glucose Meters: Glucose meters are handheld devices that provide a quick and convenient way to measure blood sugar levels. They use a small drop of blood obtained by pricking the finger with a lancet. The blood sample is then applied to a test strip, and the glucose meter provides a digital reading within seconds. Glucose meters are portable and can be easily carried around for on-the-go monitoring.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems: CGM systems provide real-time glucose monitoring by using a small sensor inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The sensor continuously sends data to a receiver or a smartphone app, allowing individuals to view their glucose levels throughout the day. CGM systems provide trend data, including information on how glucose levels change over time, and can provide alerts for low or high blood sugar levels. This technology offers a more comprehensive and detailed picture of blood sugar trends compared to traditional glucose meters.
- Flash Glucose Monitoring: Flash glucose monitoring is similar to CGM but does not require continuous real-time monitoring. Instead, individuals can scan the sensor with a reader or smartphone to obtain glucose readings at any given time. Flash glucose monitoring systems also provide trend data, including the ability to see glucose levels over several hours, helping individuals identify patterns and make informed decisions about their diabetes management.
- Insulin Pumps with Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Some insulin pumps are integrated with CGM systems, creating a closed-loop system where the pump automatically adjusts insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings. These systems can help individuals achieve better blood sugar control by providing precise insulin dosing based on glucose trends.
In addition to the tools mentioned above, individuals can adopt various techniques to optimize blood sugar monitoring:
- Regular Testing: Consistency is key. Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels throughout the day, including fasting levels, before and after meals, and before bedtime, provides valuable information about how food, physical activity, and medications impact glucose levels.
- Keeping Records: Maintaining a log or using diabetes management apps to record glucose readings, along with details about meals, physical activity, and medication, can help identify patterns and make adjustments to diabetes management plans.
- Consulting Healthcare Professionals: Working closely with healthcare professionals, such as doctors and diabetes educators, can provide guidance on blood sugar monitoring techniques, interpretation of results, and adjustments to medication or lifestyle as needed.
By utilizing appropriate monitoring tools and techniques, individuals with diabetes can stay informed about their blood sugar levels, make informed decisions about their diabetes management, and achieve better control over their condition. Regular monitoring empowers individuals to take charge of their health and make proactive choices to maintain optimal blood sugar levels.